 |
HDF5 Last Updated on 2026-02-04
The HDF5 Field Guide
|
 |
HDF5 Last Updated on 2026-02-04
The HDF5 Field Guide
|
Navigate back: Main / HDF5 User Guide
The virtual object layer is an abstraction layer in the HDF5 library that intercepts all API calls that could potentially access objects in an HDF5 container and forwards those calls to a VOL connector, which implements the storage. The user or application gets the benefit of using the familiar and widely-used HDF5 data model and API, but can map the physical storage of the HDF5 file and objects to storage that better meets the application's data needs.
The VOL lies just under the public API. When a storage-oriented public APIcall is made, the library performs a few sanity checks on the input parameters and then immediately invokes a VOL callback, which resolves to an implementation in the VOL connector that was selected when opening or creating the file. The VOL connector then performs whatever operations are needed before control returns to the library, where any final library operations such as assigning IDs for newly created/opened datasets are performed before returning. This means that, for calls that utilize the VOL, all of the functionality is deferred to the VOL connector and the HDF5 library does very little work. An important consideration of this is that most of the HDF5 caching layers (metadata and chunk caches, page buffering, etc.) will not be available as those are implemented in the HDF5 native VOL connector and cannot be easily reused by external connectors.
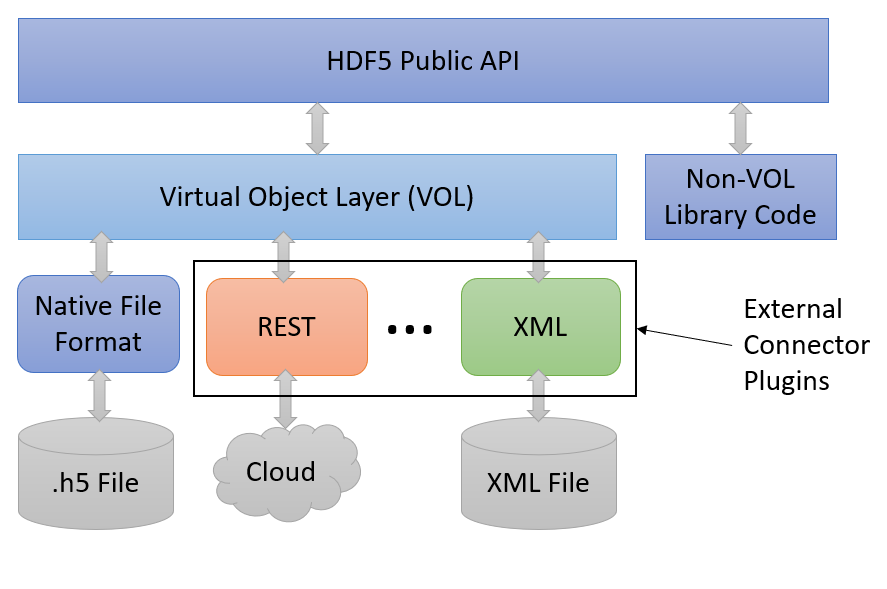
The VOL Architecture |
Not all public HDF5 API calls pass through the VOL. Only calls which require manipulating storage go through the VOL and require a VOL connector author to implement the appropriate callback. Dataspace, property list, error stack, etc. calls have nothing to do with storage manipulation or querying and do not use the VOL. This may be confusing when it comes to property list calls, since many of those calls set properties for storage. Property lists are just collections of key-value pairs, though, so a particular VOL connector is not required to set or get properties.
Another thing to keep in mind is that not every VOL connector will implement the full HDF5 public API. In some cases, a particular feature like variable-length types may not have been developed yet or may not have an equivalent in the target storage system. Also, many HDF5 public API calls are specific to the native HDF5 file format and are unlikely to have any use in other VOL connectors. A feature/capabilities flag scheme is being developed to help navigate this.
For more information about which calls go through the VOL and the mechanism by which this is implemented, see the connector author and library internals documentation.
A VOL connector can be implemented in several ways:
This section mostly focuses on external connectors, both libraries and plugins, as those are expected to be much more common than internal implementations.
A list of VOL connectors can be found here: Registered VOL Connectors
This list is incomplete and only includes the VOL connectors that have been registered with The HDF Group.
Not every connector in this collection is actively maintained by The HDF Group. It simply serves as a single location where important VOL connectors can be found. See the documentation in a connector's repository to determine its development status and the parties responsible for it.
A VOL template that contains build scripts (Autotools and CMake) and an empty VOL connector "shell" which can be copied and used as a starting point for building new connectors is located here: VOL Connector Template
This template VOL connector is for use in constructing terminal VOL connectors that do not forward calls to an underlying connector. The external pass-through VOL connector listed on the registered connector page can be used as a starting point for pass-through connectors.
The only current (non-test) internal VOL connector distributed with the library is the native file format connector (the "native VOL connector") which contains the code that handles native HDF5 (*.h5/hdf5) files. In other words, even the canonical HDF5 file format is implemented via the VOL, making it a core part of the HDF5 library and not an optional component which could be disabled.
It has not been completely abstracted from the HDF5 library, though, and is treated as a special case. For example, it cannot be unloaded and is always present.
The following steps summarize how one would go about using a VOL connector with an application. More information on particular steps can be found later on in this document.
Many VOL connectors will require specific setup and configuration of both the application and the storage. Specific permissions may have to be set, configuration files constructed, and connector-specific setup calls may need to be invoked in the application. In many cases, converting software to use a new VOL connector will be more than just a straightforward drop-in replacement done by specifying a name in the VOL plugin environment variable.
The virtual object layer was introduced in HDF5 1.12.0, however that version of the VOL is deprecated due to inadequate support for pass-through connectors. These deficiencies have been addressed in HDF5 1.14.0, so VOL users and connector authors should target the 1.14.0 VOL API.
On Windows, it's probably best to use the same debug vs release configuration for the application and all libraries in order to avoid C runtime (CRT) issues. Pre-2015 versions of Visual Studio are not supported.
Fundamentally, setting a VOL connector involves modifying the file access property list (fapl) that will be used to open or create the file.
There are essentially three ways to do this:
Exactly how you go about setting a VOL connector in a fapl, will depend on the complexity of the VOL connector and how much control you have over the application's source code. Note that the environment variable method, though convenient, has some limitations in its implementation, which are discussed below.
There are two concerns when modifying the application:
In some cases, using the VOL environment variable will work well for setting the connector and any associated storage setup and the application will not use API calls that are not supported by the VOL connector. In this case, no application modification will be necessary.
Path The default location for all HDF5 plugins is set at configure time when building the HDF5 library. This is true for both CMake and the Autotools. The default locations for the plugins on both Windows and POSIX systems is listed further on in this document.
In place of modifying the source code of your application, you may be able to simply set the HDF5_VOL_CONNECTOR environment variable (see below). This will automatically use the specified VOL in place of the native VOL connector.
Before a VOL connector can be set in a fapl, it must be registered with the library (H5Pset_vol requires the connector's hid_t ID) and, if a plugin, it must be discoverable by the library at run time.
Before a connector can be used, it must be registered. This loads the connector into the library and give it an HDF5 hid_t ID. The H5VLregister_connector API calls are used for this.
When used with a plugin, these functions will check to see if an appropriate plugin with a matching name, value, etc. is already loaded and check the plugin path (see above) for matching plugins if this is not true. The functions return H5I_INVALID_HID if they are unable to register the connector. Many VOL connectors will provide a connector-specific init call that will load and register the connector for you.
Note the two ways that a VOL connector can be identified: by a name or by a connector-specific numerical value (H5VL_class_value_t is typedef’d to an integer). The name and value for a connector can be found in the connector's documentation or public header file.
Each call also takes a VOL initialization property list (vipl). The library adds no properties to this list, so it is entirely for use by connector authors. Set this to H5P_DEFAULT unless instructed differently by the documentation for the VOL connector.
As far as the library is concerned, connectors do not need to be explicitly unregistered as the library will unload the plugin and close the ID when the library is closed. If you want to close a VOL connector ID, either H5VLunregister_connector() or H5VLclose() can be used (they have the same internal code path). The library maintains a reference count on all open IDs and will not do the actual work of closing an ID until its reference count drops to zero, so it's safe to close IDs anytime after they are used, even while an HDF5 file that was opened with that connector is still open.
Note that it's considered an error to unload the native VOL connector. The library will prevent this. This means that, for the time being, the native VOL connector will always be available. This may change in the future so that the memory footprint of the native VOL connector goes away when not in use.
The VOL connector struct provides a conn_version field for versioning connectors. The library developers are working on some best practices for versioning connectors.
Most connectors will provide a special API call which will set the connector in the fapl. These will often be in the form of H5Pset_fapl_<name>(). For example, the DAOS VOL connector provides a H5Pset_fapl_daos() API call which will take MPI parameters and make this call. See the connector's documentation or public header file(s) for more information.
The is the main library API call for setting the VOL connector in a file access property list. Its signature is:
It takes the ID of the file access property list, the ID of the registered VOL connector, and a pointer to whatever connector-specific data the connector is expecting. This will usually be a data struct specified in the connector's header or a NULL pointer if the connecter requires no special information (as in the native VOL connector).
As mentioned above, many connectors will provide their own replacement for this call. See the connector's documentation for more information.
Dynamically loaded VOL connector plugins are discovered and loaded by the library using the same mechanism as dataset/group filter plugins. The default locations are:
Default locations
These default locations can be overridden by setting the HDF5_PLUGIN_PATH environment variable. There are also public H5PL API calls which can be used to add, modify, and remove search paths. The library will only look for plugins in the specified plugin paths. By default, it will NOT find plugins that are simply located in the same directory as the executable.
Each VOL connector is allowed to take in a parameter string which can be parsed via H5VLconnector_str_to_info() to get an info struct which can be passed to H5Pset_vol().
And the obtained info can be freed via:
Most users will not need this functionality as they will be using either connector- specific setup calls which will handle registering and configuring the connector for them or they will be using the environment variable (see below).
The HDF5 library allows specifying a default VOL connector via an environment variable: HDF5_VOL_CONNECTOR. The value of this environment variable should be set to ”vol connector name <parameters>”.
This will perform the equivalent of:
The environment variable is parsed once, at library startup. Since the environment variable scheme just changes the default connector, it can be overridden by subsequent calls to H5Pset_vol(). The <parameters> is optional, so for connectors which do not require any special configuration parameters you can just set the environment variable to the name.
NOTE: Implementing the environment variable in this way means that setting the native VOL connector becomes somewhat awkward as there is no explicit HDF5 API call to do this. Instead you will need to get the native VOL connector's ID via H5VLget_connector_id_by_value(H5_VOL_NATIVE) and set it manually in the fapl using H5Pset_vol().
The VOL was engineered to be as unobtrusive as possible and, when a connector which implements most/all of the data model functionality is in use, many applications will require little, if any, modification. As mentioned in the quick start section, most modifications will probably consist of connector setup code (which can usually be accomplished via the environment variable), adapting code to use the new token-based API calls, and protecting native-VOL-connector-specific functions.
Some HDF5 API calls and data structures refer to addresses in the HDF5 using the haddr_t type. Unfortunately, the concept of an ”address” will make no sense for many connectors, though they may still have some sort of location key (e.g.: a key in a key-value pair store).
As a part of the VOL work, the HDF5 API was updated to replace the haddr_t type with a new H5O_token_t type that represents a more generic object location. These tokens appear as an opaque byte array of H5O_MAX_TOKEN_SIZE bytes that is only meaningful for a particular VOL connector. They are not intended for interpretation outside of a VOL connector, though a connector author may provide an API call to convert their tokens to something meaningful for the storage.
As an example, in the native VOL connector, the token stores an haddr_t address and addresses can be converted to and from tokens using H5VLnative_addr_to_token() and H5VLnative_token_to_addr().
Several API calls have also been added to compare tokens and convert tokens to and from strings.
H5Fis_hdf5() does not take a file access property list (fapl). As this is where the VOL connector is specified, this call cannot be used with arbitrary connectors. As a VOL-enabled replacement, H5Fis_accessible() has been added to the library. It has the same semantics as H5Fis_hdf5(), but takes a fapl so it can work with any VOL connector.
Note that, at this time, H5Fis_hdf5() always uses the native VOL connector, regardless of the settings of environment variables, etc.
Note also that an error is only returned if it is not possible to determine if a file (or container) is accessible. It is not an error to return 'false' for whether the file is accessible.
The H5Oget_info1() and H5Oget_info2() family of HDF5 API calls are often used by user code to obtain information about an object in the file, however these calls returned a struct which contained native information and are thus unsuitable for use with arbitrary VOL connectors.
A new H5Oget_info3() family of API calls has been added to the library which only return data model information via a new H5O_info2_t struct. This struct also returns H5O_token_t tokens in place of haddr_t addresses.
To return the native file format information, H5Oget_native_info() calls have been added which can return such data separate from the data model data.
The callback used in the H5Ovisit() family of API calls took an H5O info t struct parameter. As in H5Oget_info(), this both commingled data model and native file format information and also used native HDF5 file addresses.
New H5Ovisit3() API calls have been created which use the token-based, data-model-only H5O_info_t struct in the callback.
The H5Lget_info() API calls were updated to use tokens instead of addresses in the H5L_info_t struct.
The callback used in these API calls used the old H5L_info_t struct, which used addresses instead of tokens. These callbacks were versioned in the C library and now take modified H5L_iterate2_t callbacks which use the new token-based info structs.
The new H5Oopen_by_token() API call can be used to open objects by the tokens that are returned by the various ”get info”, et al. API calls.
In HDF5 1.14.0, a way to determine support for optional calls has been added.
The call takes an object that is VOL managed (i.e.; file, group, dataset, attribute, object, committed datatype), the VOL subclass (an enum documented in H5VLpublic.h), an operation ”type” (discussed below), and an out parameter for the bitwise capabilities flags (also discussed below). Code that needs to protect a VOL-specific API call can call the function to see if the API call is supported, which will be reported via the flags. Specifically, if the H5VL_OPT_QUERY_SUPPORTED bit is set, the feature is supported. The other flags are more useful for VOL connector authors than end users.
In the case of the native VOL connector, the opt type operations are documented in H5VLnative.h. The current list of native operations is given at the end of this document, along with a list of native-only connector calls.
Due to the parameter type and callback changes that were required in the C library API regarding the update from haddr_t addresses to H5O_token_t tokens and the difficulty in versioning the wrapper APIs, it was decided to update all of the wrappers to use tokens instead of addresses. This will allow the language wrappers to make use of the VOL, but at the expense of backward compatibility.
Information on the C API changes can be found above.
Affected API calls, by language:
The C++ wrappers do not allow opening HDF5 file objects by address or token.
The public H5VL API calls found in H5VLpublic.h were NOT added to the C++ API.
As in the C API, these API calls had their structs updated to the token version so the h5o_info_t, etc. structs no longer contain native file format information and the callbacks will need to match the non-deprecated, token-enabled versions.
Additionally, h5fis_hdf5_f was updated to use H5Fis_accessible internally, though with the same caveat as the C++ implementation: the default fapl is always passed in so arbitrary VOL connectors will only work if the default VOL connector is changed via the environment variable.
The public H5VL API calls found in H5VLpublic.h were also added to the Fortran wrappers.
The following command-line tools are VOL-aware and can be used with arbitrary VOL connectors:
The VOL connector can be set either using the HDF5_VOL_CONNECTOR environment variable (see above) or via the command line. Each of the above tools takes command-line options to set the VOL connector by name or value and the VOL connector string, usually in the form of
See the individual tool's help for the options specific to that tool.
These API calls will probably fail when used with terminal VOL connectors other than the native HDF5 file format connector. Their use should be protected in code that uses arbitrary VOL connectors. Note that some connectors may, in fact, implement some of this functionality as it is possible to mimic the native HDF5 connector, however this will probably not be true for most non-native VOL connectors.
These HDF5 API calls do not depend on a particular VOL connector being loaded.
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| H5* | |
| H5Dfill | |
| H5Dgather | |
| H5Diterate | |
| H5Dscatter | |
| H5Dvlen_reclaim | deprecated |
| H5Dvlen_get_buf_size | |
| H5E* | |
| H5I* | |
| H5Lis_registered | |
| H5Lregister | |
| H5Lunpack_elink_val | |
| H5Lunregister | |
| H5PL* | |
| H5P* | |
| H5S* | |
| H5T* | non-committed |
| H5VL* | |
| H5Z* |
These values can be passed to the opt type parameter of H5VLquery optional().
Previous Chapter Properties and Property Lists in HDF5 - Next Chapter The HDF5 Event Set Interface
Navigate back: Main / HDF5 User Guide