 |
HDF5 1.14.6
API Reference
|
 |
HDF5 1.14.6
API Reference
|
Navigate back: Main / Getting Started with HDF5 / Learning the Basics
There are two ways that you can select a subset in an HDF5 dataset and read or write to it:
HDF5 allows you to read from or write to a portion or subset of a dataset by:
First you must obtain the dataspace of a dataset in a file by calling H5Dget_space.
Then select a subset of that dataspace by calling H5Sselect_hyperslab. The offset, count, stride and block parameters of this API define the shape and size of the selection. They must be arrays with the same number of dimensions as the rank of the dataset's dataspace. These arrays ALL work together to define a selection. A change to one of these arrays can affect the others.
You must select a memory dataspace in addition to a file dataspace before you can read a subset from or write a subset to a dataset. A memory dataspace can be specified by calling H5Screate_simple.
The memory dataspace passed to the read or write call must contain the same number of elements as the file dataspace. The number of elements in a dataspace selection can be determined with the H5Sget_select_npoints API.
To read from or write to a dataset subset, the H5Dread and H5Dwrite routines are used. The memory and file dataspace identifiers from the selections that were made are passed into the read or write call. For example (C):
See Examples from Learning the Basics for the examples used in the Learning the Basics tutorial.
The example creates an 8 x 10 integer dataset in an HDF5 file. It then selects and writes to a 3 x 4 subset of the dataset created with the dimensions offset by 1 x 2. (If using Fortran, the dimensions will be swapped. The dataset will be 10 x 8, the subset will be 4 x 3, and the offset will be 2 x 1.)
PLEASE NOTE that the examples and images below were created using C.
The following image shows the dataset that gets written originally, and the subset of data that gets modified afterwards. Dimension 0 is vertical and Dimension 1 is horizontal as shown below:
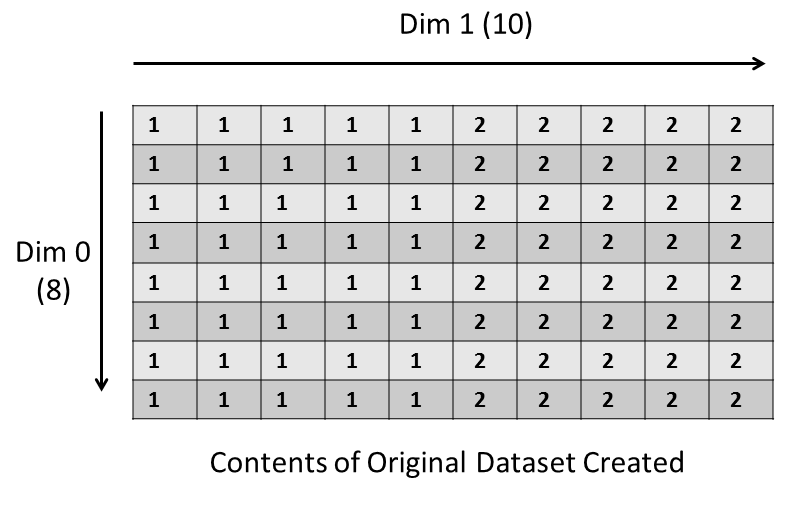
|
The subset on the right above is created using these values for offset, count stride, and block:
Following are examples of changes that can be made to the example code provided to better understand how to make selections.
By default the example code will select and write to a 3 x 4 subset. You can modify the count parameter in the example code to select a different subset, by changing the value of DIM0_SUB (C, C++) / dim0_sub (Fortran) near the top. Change its value to 7 to create a 7 x 4 subset:
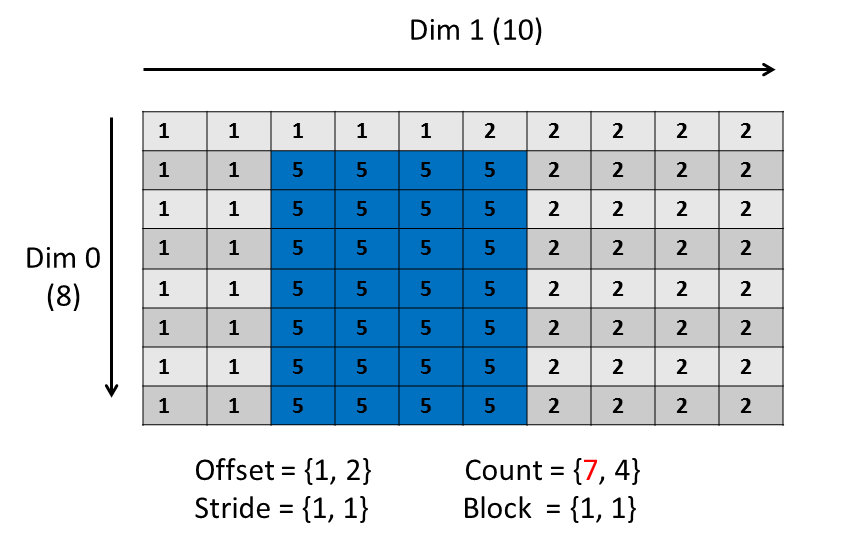
|
If you were to change the subset to 8 x 4, the selection would be beyond the extent of the dimension:
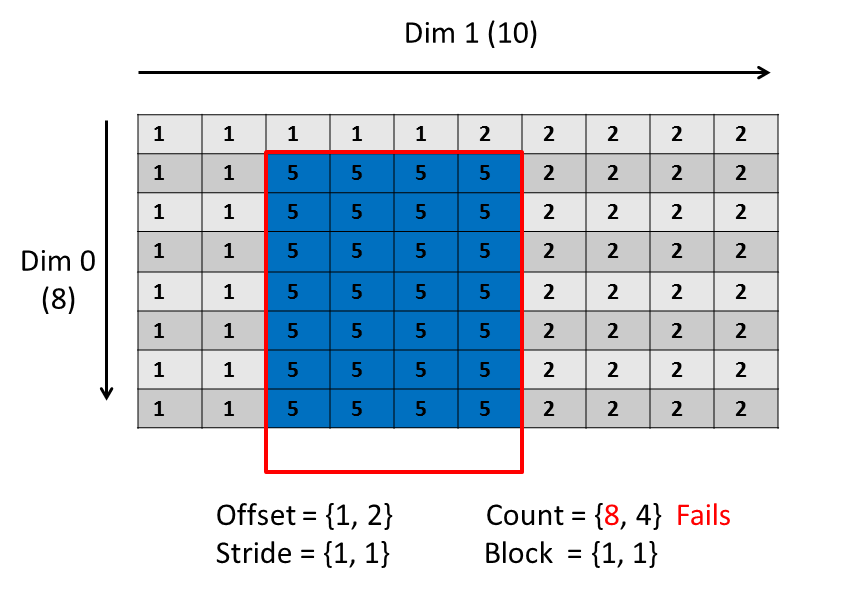
|
The write will fail with the error: "<strong>file selection+offset not within extent</strong>"
In the example code provided, the memory and file dataspaces passed to the H5Dwrite call have the same size, 3 x 4 (DIM0_SUB x DIM1_SUB). Change the size of the memory dataspace to be 4 x 4 so that they do not match, and then compile:
The code will fail with the error: "<strong>src and dest data spaces have different sizes</strong>"
How many elements are in the memory and file dataspaces that were specified above? Add these lines:
You should see these lines followed by the error:
This example shows the selection that occurs if changing the values of the offset, count, stride and block parameters in the example code.
This will select two blocks. The count array specifies the number of blocks. The block array specifies the size of a block. The stride must be modified to accommodate the block size.
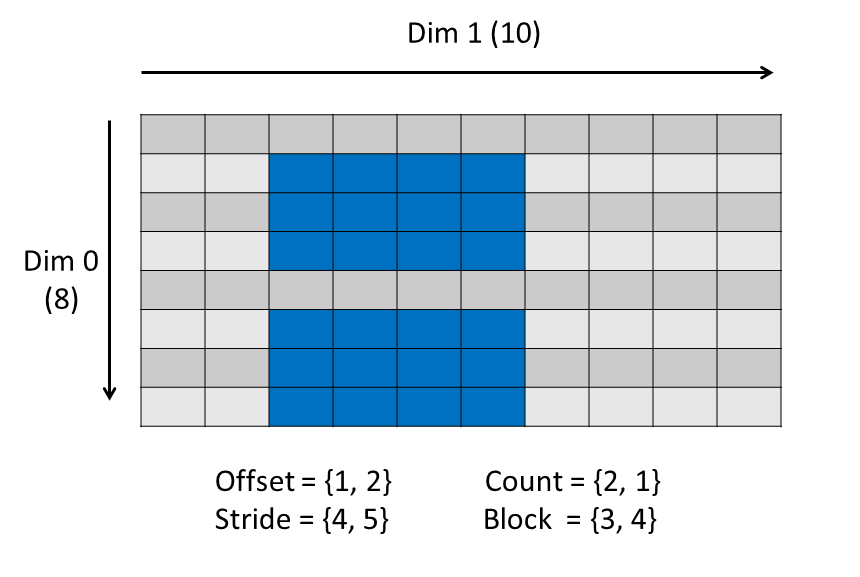
|
Now try modifying the count as shown below. The write will fail because the selection goes beyond the extent of the dimension:
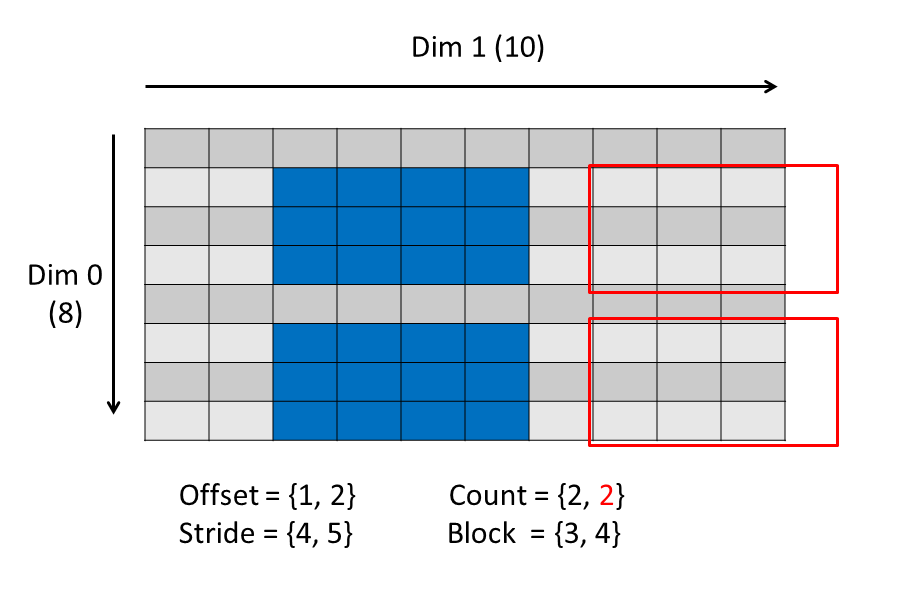
|
If the offset were 1x1 (instead of 1x2), then the selection can be made:
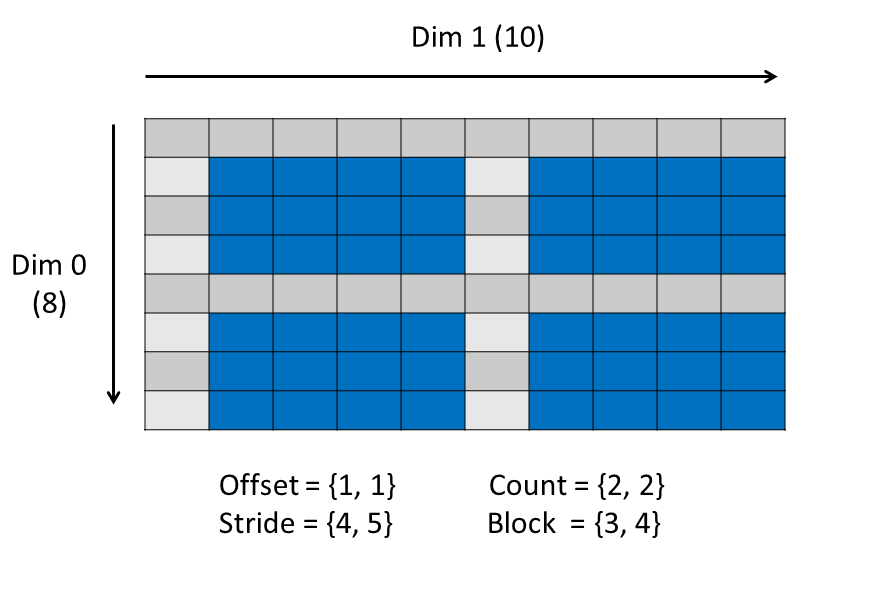
|
The selections above were tested with the h5_subsetbk.c example code. The memory dataspace was defined as one-dimensional.
Previous Chapter Creating Datasets in Groups - Next Chapter Datatype Basics
Navigate back: Main / Getting Started with HDF5 / Learning the Basics